

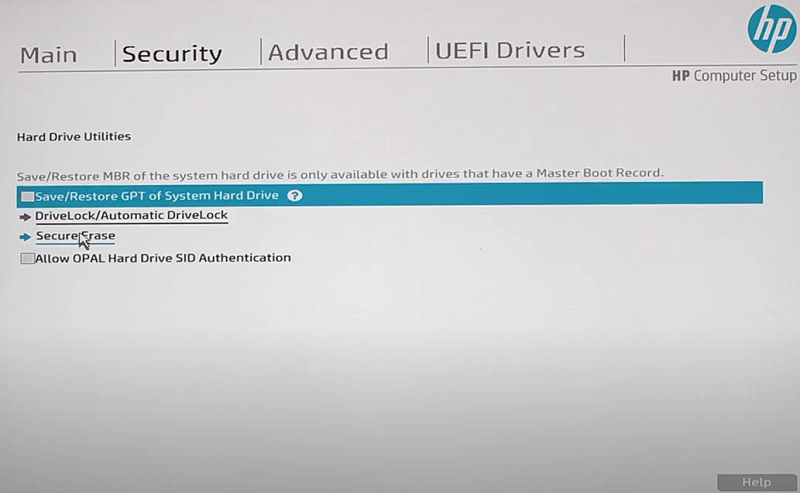
Solution 4: How to Erased Hard Drive with SDelete.Solution 3: How to Erase Hard Drive with Ccleaner.Solution 2: Darik's Boot and Nuke (DBAN).Solution 1: Erase the Hard drive with HDDErase.Be sure to always be safe with your data and move on from the fears created during the HDD age.Ĭheck the NVM Express site for more information on NVMe-CLI. Drives supporting hardware encryption may also enjoy the additional cryptographic erase option. Additionally functions may or may not be activated - depending on the controller - however our utility designed for sector resizing is based on the NVMe format command.

We only sell NVMe SSDs and as they follow the NVMe specification they can be safely erased. The old requirement to overwrite data, as used with Department of Defense schema, is therefore not required for SSDs. Some data may be outside of the user space or in unerasable blocks, however even this is accounted for on modern drives and forensic data retrieval is complex even under the best circumstances. Erasing the cells is very effective at destroying any traces of the previously-existing data. How secure is this? SSDs, unlike HDDs, are designed for performance with cells that must be erased before new data can be written. This helps return the drive to a fresh-out-of-the-box (FOB) state with the first step being potentially faster than waiting for a full erase. This can be followed up by a sanitize block erase which works similarly to blkdiscard. This exposes additional features the SSD might have, for example the ability to simply delete the encryption key on a Self-Encrypting Drive (SED), using 256-bit AES, with the cryptographic scramble command. Linux has some powerful tools for this with the NVMe command line interface (nvme-cli). It’s also possible to use other software, including bootable software and operating systems, to clean the drive. SSDs with software support in the form of a toolbox, like ours, may have a Secure Erase feature built-in. In a modern OS like Windows, in fact, a quick format will act like a Secure Erase and the drive will require sufficient idle time to actually clear the drive. Modern SSDs treat these functions very similarly, although it can take a few minutes for the drive to bulk erase the cells. Translating Logical Block Addresses (LBA) to Physical Block Addresses (PBA) What’s the difference? If we avoid talking about hard disk drives (HDD) and acknowledge SSDs work differently, a Secure Erase wipes the mapping or address table of the drive while the Sanitize additionally erases the cells immediately. In either case, it’s a good policy to engage in a Secure Erase or Sanitize function to be sure the drive is clean. Other times, they want to migrate or sell their SSD and want to make sure existing data cannot be retrieved. Sometimes users want to return their drives to a like-new condition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
